The word ‘exosomes’ seems to be on everybody’s lips these days, having emerged as a prominent topic of interest in various industries. While their existence was first identified in mammalian cells back in 1983, it is only now that scientists are unravelling their true applications. And the implications could be huge. Extensive research is being conducted in diverse sectors such as drug delivery, nutrition, chemical diagnostics, therapeutics, and even cancer prevention. In the field of aesthetics, they are creating excitement, too, offering novel and exciting possibilities due to their remarkable regenerative properties, anti-inflammatory effects, and use alongside energybased devices to speed up healing and minimise recovery time.
Dr Rob King, the National Director of Biologics & Aesthetic Management Partners, spoke about the topic at Wigmore Presents and introduced a plant-based alternative to exosomes known as plant-derived extracellular nanoparticles (PDENs) to delegates.
Decoding exosomes: the cellular couriers
Exosomes are minuscule extracellular vesicles that are naturally generated and can be derived from plants, animals, or humans. Enclosed within a lipid membrane, these nanoscale sacs play a pivotal role in facilitating intercellular communication.
Acting as messengers, they transport signalling molecules like proteins and genetic material between cells, thereby influencing essential biological processes. When they come across cells in need of repair, they trigger the restoration process, setting in motion the wheels of cellular rejuvenation.
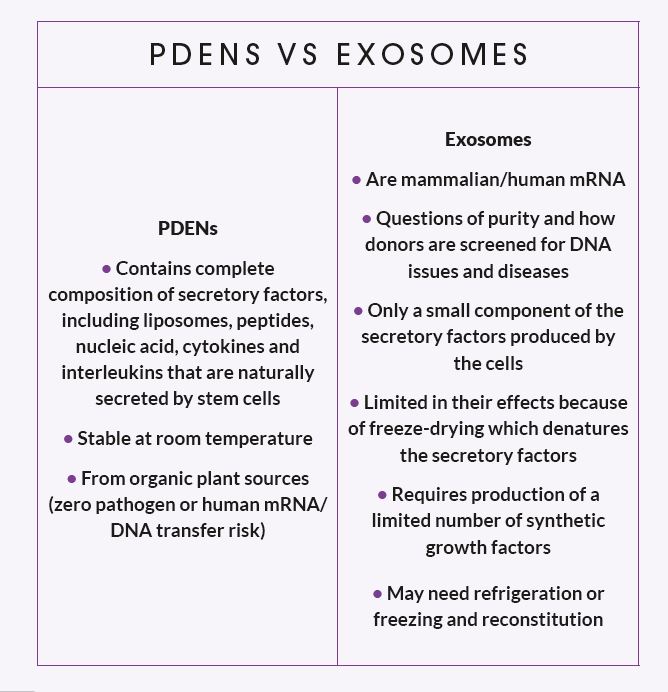
However, the usage of human-derived exosomes has raised concerns, particularly in the UK where the use of human-derived ingredients is prohibited. While some people are using topical exosome applications, under the rational that it is permissible as long as they are not injected, the legality of such practices remains questionable.
Regulatory and safety concerns contribute to the hesitation surrounding human-derived exosomes. Since exosomes are derived from cells, it is imperative to establish standardised manufacturing processes and quality control measures to ensure their safety, efficacy, and reproducibility.
Additionally, thorough evaluation of the potential off-target effects or unintended consequences of exosome-based therapies is still ongoing. This is where plant-based alternatives offer an exciting opportunity.
Plant-based exosomes: The rise of PDENs
PDENs are extracted from plant stem cells and represent the botanical counterpart to human exosomes.
In simple terms, PDENs are envelopes that facilitate cell-to-cell communication. Over the past decade, research has unveiled that plant stem cells produce human cytokine-like factors that enable the use of plant secretory factors for human cell signalling.
For aesthetic applications, this means scientists can load these envelopes with thousands of biomimetic factors, including growth factors, peptides, liposomes, amino acids, and proteins directed explicitly to target inflammation as well as for wound healing angiogenesis and the stimulation of hyaluronic acid, collagen and elastin production.
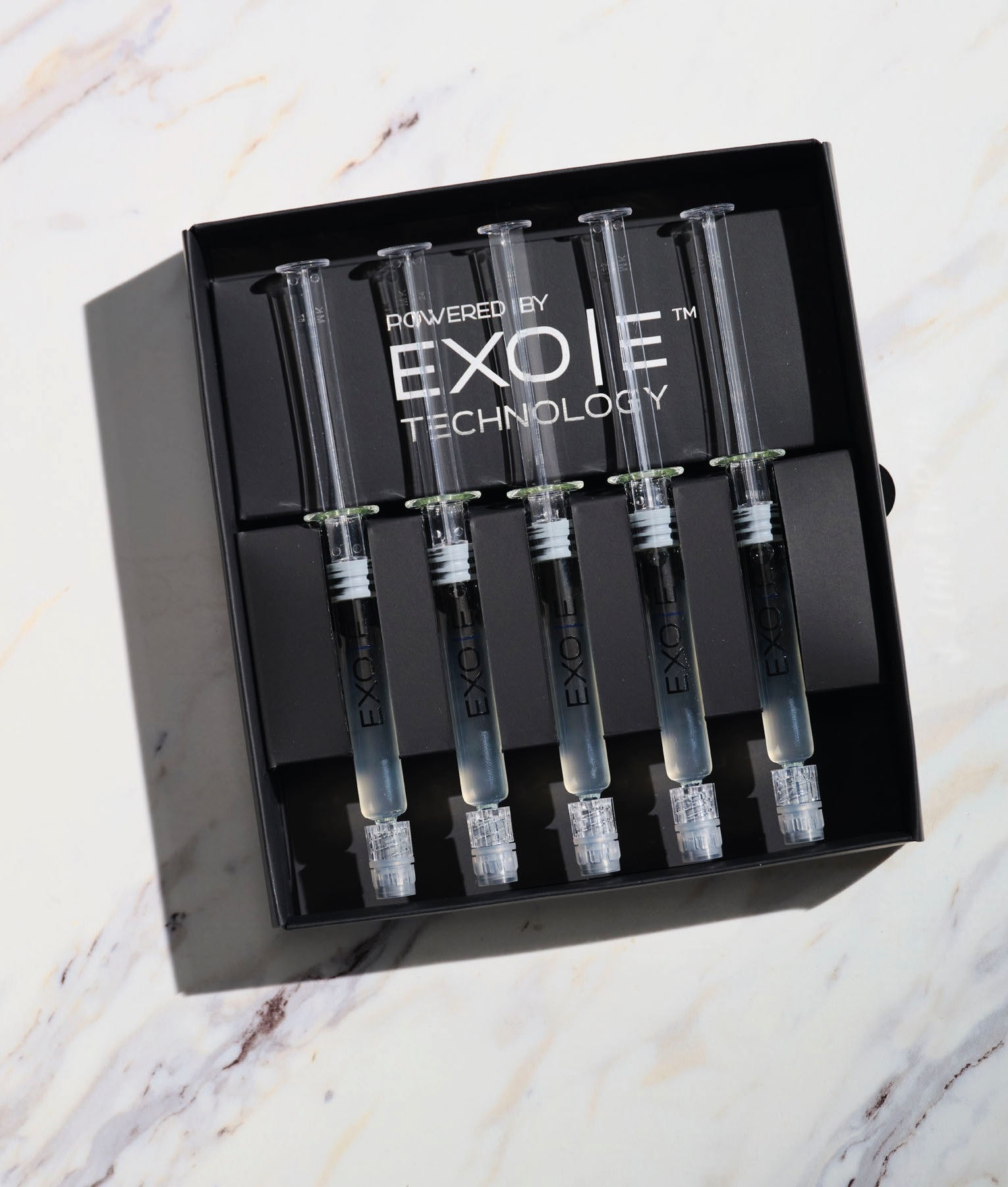
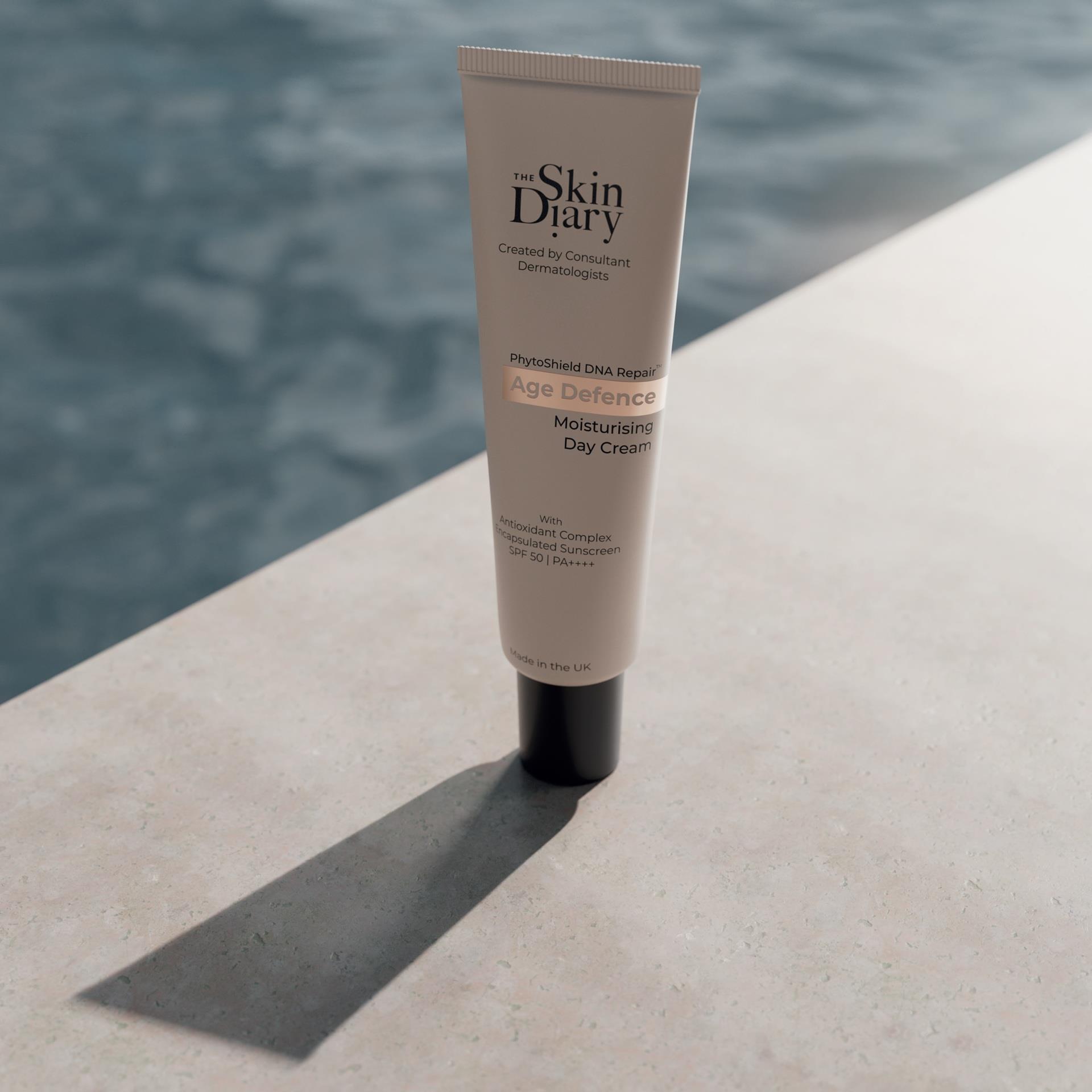
Introducing EXO|E Revitalizing Complex
Aesthetic Medical Partnership (AMP) has recently launched EXO|E Revitalizing Complex, a cutting-edge skincare solution that harnesses the power of biomimetic plant stem cell technology to rejuvenate and revitalise the skin.
This unique bio-based patented technology ensures flawless compatibility with the skin, providing exceptional support and supplementation to its natural signalling mechanism, leading to optimal rebalancing effects.
Traditional rejuvenation procedures often induce inflammation, causing pain, swelling, redness, extended downtime, and undesirable side effects that leave patients with a negative experience or hesitancy to repeat the treatment, EXO|E offers a paradigm shift in the healing process. By redirecting the focus from inflammation to rejuvenation, EXO|E minimises downtime while delivering enhanced treatment results.
Suitable for all skin types and conditions, the comprehensive treatment protocol consists of three steps: D|TOX, EXO|E, and RE|PAIR. These steps can be seamlessly incorporated into both inclinic and at-home routines, whether it's to prepare the skin before a procedure or to amplify treatment outcomes.
Furthermore, EXO|E can also be used as a stand-alone treatment, offering versatility and convenience for individuals seeking a singular skincare solution.
"One of the advantages of EXO|E lies in its exceptional ability to penetrate the skin transdermally through lipophilic absorption"
The three-step process of EXO|E
1. D|TOX: This step provides deep hydration and prepares the skin for subsequent aesthetic treatments, ensuring optimal efficacy.
2. EXO|E serum: Packed with concentrated stem cell factors, this serum delivers targeted and desired outcomes, effectively revitalising the skin.
3. RE|PAIR serum: Working in synergy with EXO|E, this serum reinforces the effects with additional extracellular nanoparticle technology and liposomes, maximising the benefits
of the treatment.
Clinical use
One of the advantages of EXO|E lies in its exceptional ability to penetrate the skin transdermally through lipophilic absorption. This enables a comprehensive treatment approach, reaching and addressing the entire dermal architecture with efficient cell-to-cell signalling.
Studies also show that EXO|E increases collagen and elastin production by 165 per cent and 891% per cent respectively, as well as increasing the secretion of hyaluronic acid by 198 per cent and providing a 61 per cent daily reduction in inflammation.
Miss Sherina Balaratnam, surgeon, cosmetic doctor and medical director of S-Thetics Clinic, was the first to introduce the productto her clinic. She says, “I am excited to be the first clinic in the UK and Europe and one of the first globally, outside of the US, to introduce the UK’s first completely plant-derived exosome product.
“I have spent over eight years understanding ingredient formulations and the science behind how botanically-derived topical skincare works. I have curated bespoke protocols with these topicals to produce highly regenerative results for my patients.
“Together with my previous knowledge and understanding of cell signalling from my research time at the University College of London (UCL 2004-5), these learnings have developed my knowledge of regenerative skin science.
“EXO|E delivers the next phase of topicals to fill in the missing links, such as the regeneration of one’s own elastin, hyaluronic acid and collagen production, up-regulated endogenously.
“This is only the second skincare system I have introduced to my clinic after eight years, illustrating the depth and breadth of the robust science, clinical validation and manufacturing processes behind EXO|E.”
EXO|E Revitalizing Complex represents a ground-breaking advancement in the field of skincare, delivering unparalleled rejuvenation and revitalisation. Its transformative effects are rooted in the power of plant-based exosomes, setting a new standard for comprehensive and effective skin treatments.
EXO|E is now exclusively available at Wigmore Medical. It comes as a pack of 10 treatments which includes 10 packets of 10 D|TOX ampoules for twice daily application for five days before treatment (contains four billion PDENs), one box of 10 syringes of EXO|E extracellular complex for application in clinic either as treatment or prior to use with any other treatment. Can be applied before any topical anaesthetic (each syringe contains 15 billion PDENs) and 10 packets of 10 RE|PAIR ampoules for twice daily application for five days following treatment (contains five billion PDENs). To order, contact Customer Services on 020 7491 0150 or email orders@wigmoremedical.com
References
1. Teng Y, Xu F, Zhang X, et al. Plant-derived exosomal microRNAs inhibit lung inflammation induced by exosomes SARS-CoV-2 Nsp12. Mol Ther. 2021;29(8):2424-2440.doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.05.005
2. Cui Y, Gao J, He Y, Jiang L. Plant extracellular vesicles. Protoplasma. 2020;257(1):3-12.doi:10.1007/s00709-019-01435-6
3. Dad HA, Gu TW, Zhu AQ, Huang LQ, Peng LH. Plant Exosome-like Nanovesicles: Emerging Therapeutics and Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms. Mol Ther. 2021;29(1):13-31.doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.11.030
4. Karamanidou, T.; Tsouknidas, A. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutic Nanocarriers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010191

 Added to basket
Added to basket

 Unapplied Changes
Unapplied Changes