When it comes to optimal ageing and cellular repair, there’s one powerful category that stands out: DNA repair enzymes—biological molecules that help support the skin’s ability to repair.
What are DNA repair enzymes?
DNA repair enzymes are proteins that play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of our skin’s DNA by identifying and correcting various types of damage. We know that 80% of skin ageing is caused by UV exposure, which in turn, causes DNA damage. If not corrected, it can cause permanent DNA mutations. Our bodies can correct some of this damage itself, but as we age, our ability to do so declines. That’s where these DNA repair enzymes come in.
The Skin Diary’s latest innovation uses two types of DNA repair enzymes: Photolyase and UV Endonuclease.
Photolyase: Photolyase is an enzyme that we lost our ability to produce through evolution, meaning we need help using the Photolyase produced by plants and some animals to help repair our DNA. When UV hits our skin, it causes small breaks (or chinks) in our DNA helix called cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs). The job of Photolyase is to find these chinks in our DNA amour, wait for a photon of light to give it energy and activate it to repair instantly that CPD damage. This is called photoreactivation.
UV Endonuclease: The second type is UV Endonuclease, which works to stimulate our natural DNA to repair and boost it. One of the natural ways of repairing DNA is through something called nucleotide excision repair (NER), but as we age, our DNA repair isn’t as good. UV Endonuclease comes in to enhance our natural NER. It doesn’t require light (as Photolyase does) to work, but it does take slightly longer to repair.
Together, these are a highly effective repair system.
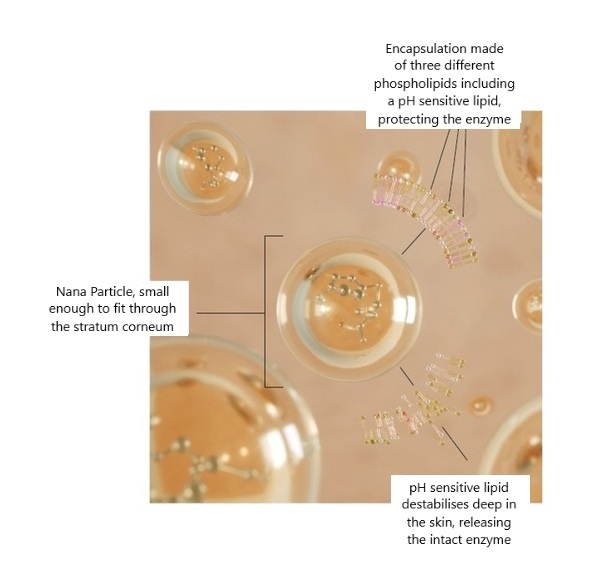
In order for DNA repair enzymes to work, they’re liposomically encapsulated, which allows them to pass the stratum corneum and get to work in DNA for cellular repair.
DNA repair enzymes and ageing skin
Since premature ageing is largely down to UV damage, focusing on preventing and mitigating this damage, through sun protection and DNA repair enzymes, improves not only skin health, but also signs of ageing such as wrinkles, hyperpigmentation and loss of elasticity.
Sunscreen works to prevent UV damage from occurring while DNA repair enzymes work to correct and minimise the harm that’s occurred.
In addition to this, research has shown that regular use of DNA repair enzymes in skincare can reduce actinic keratoses. These rough, scaly patches that are caused by long-term sun exposure. A study found that applying a lotion containing these enzymes significantly lowered the number of new actinic keratoses—and even helped some existing ones regress.
Using DNA repair enzymes as part of a skin protection routine (that includes sun safety behaviours and sunscreen) helps to optimise skin health as we age.
How much damage can DNA repair enzymes fix?
It’s important to note that while DNA repair enzymes can mitigate past UV damage, it cannot fully reverse structural changes in the skin (as much as we wish it did). The main aim is to target specific DNA damage,
such as CPDs and repair them before permanent mutations occur.
Over time, this helps to minimise signs of photoageing, reduce cellular mutations and improve overall skin health. They act as a quality control to help keep your cells in check.
To purchase login to your Wigmore Medical Account
The future of DNA repair enzymes
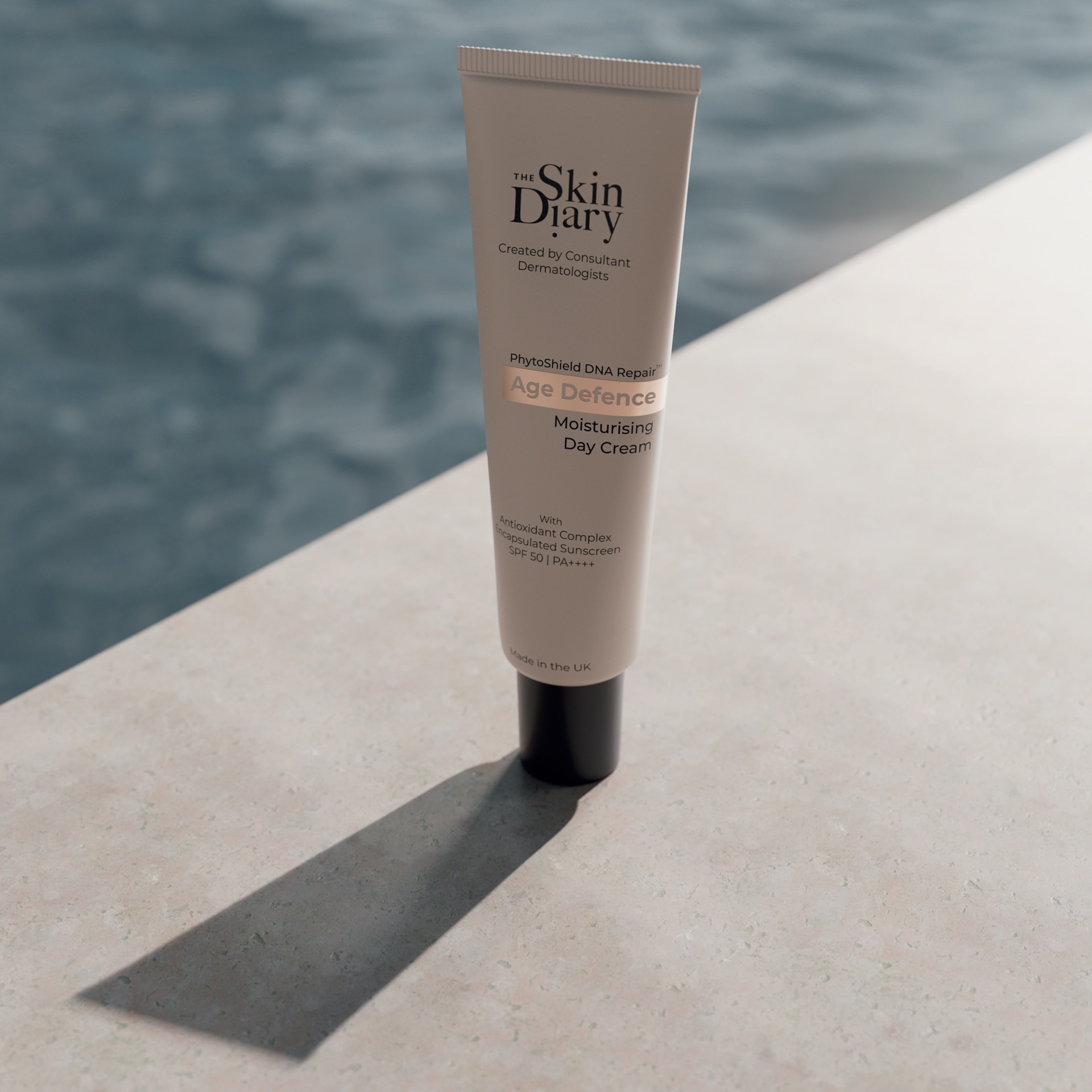
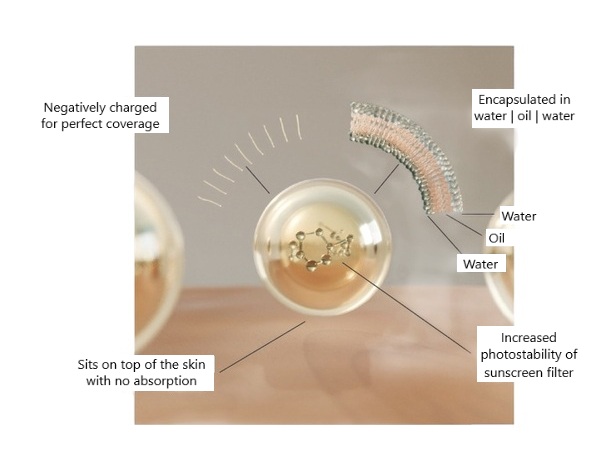
The Skin Diary Age Defence Moisturising Day Cream contains the DNA repair enzyme duo Photolyase, UV Endonuclease, plus encapsulated sunscreen SPF50 PA++++, and antioxidants—acting as a triple action defence system. Our formula was put through advanced gene expression testing, to measure its true impact on epigenetic ageing, cellular senescence and oxidative stress; three key biological pathways.
This research was independently carried out by Professor Mark Birch-Machin, a Professor of molecular dermatology and widely recognised as a leading expert in UV-induced cellular damage to human skin and skinageing. We discovered:
Age Defence Prevents UV-induced Cellular
Senescence: Giving statistically significant protection against UV-induced P21 expression;
Age Defence prevents UV-induced inflammation: Complete reduction of PTGES expression to baseline levels following UV exposure;
Age Defence prevents the breakdown of collagen, and fibrillin (elastin): Prevents the UV-induced spike in MMP1.
Statistically significant complete protection proven in gene expression analysis on 3D skin equivalents exposed to high intensity UV radiation. References: 1.Garcia-Mouronte, E.; Pérez-González, L.A.; Naharro-Rodriguez, J.; Fernández Guarino, M.
Understanding Active Photoprotection: DNA-Repair Enzymes and Antioxidants. Life 2024, 14, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070822 2. DeBoyes T, Kouba D, Ozog D, Fincher E, Moy L, Iwata K, Moy R.
Reduced number of actinic keratoses with topical application of DNA repair enzyme creams. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010 Dec;9(12):1519-21. PMID: 21120260 3. Yarosh DB, Rosenthal A, Moy R.
Six critical questions for DNA repair enzymes in skincare products: a review in dialog. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019 Aug 29;12:617-624. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S220741. PMID: 31695467;PMCID: PMC6718248

 Added to basket
Added to basket

 Unapplied Changes
Unapplied Changes